What is Oxidative Stress? The cause, effects and prevention of it
Share
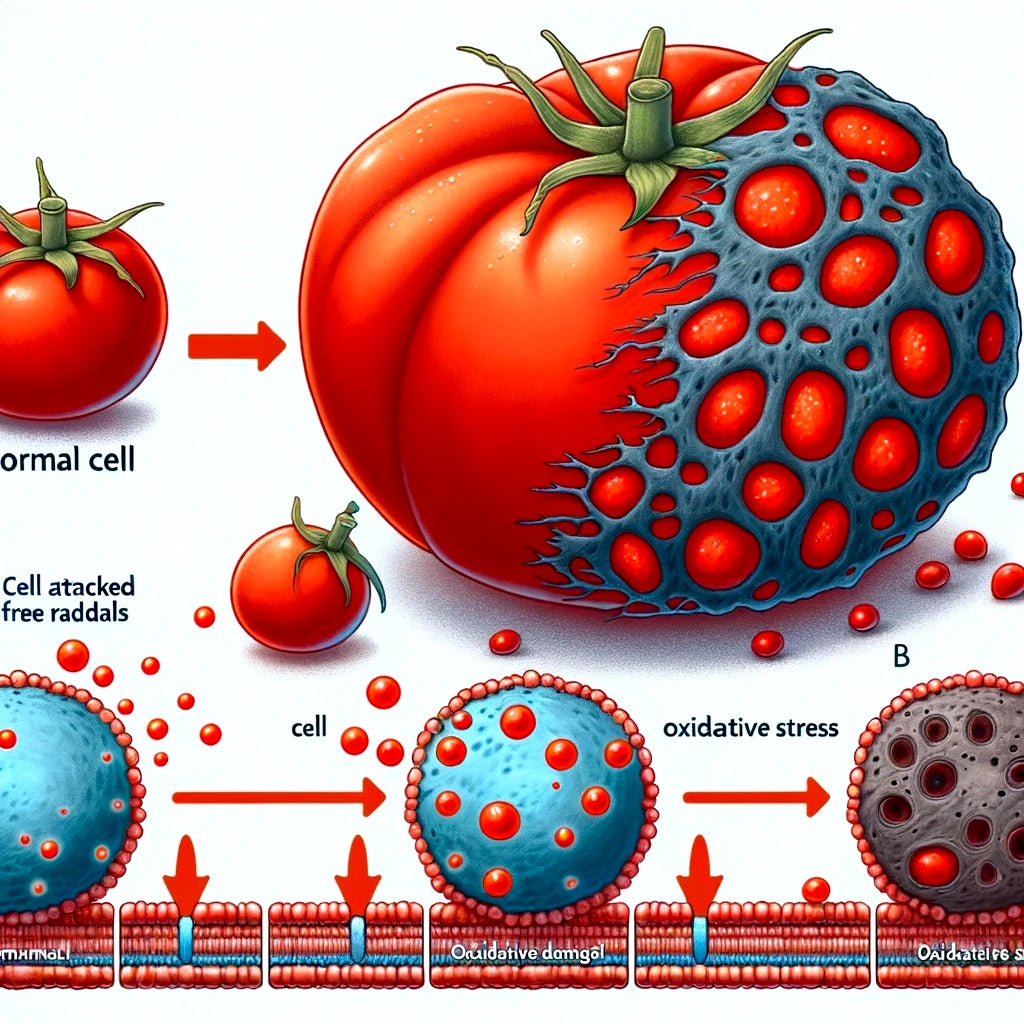
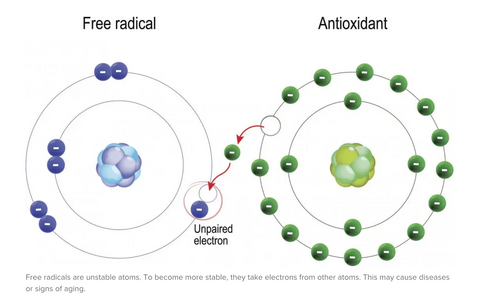
Oxidative stress is a condition that occurs when there's an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of electrons, allowing them to easily react with other molecules. While the body requires free radicals for processes like fighting infections, their excess can lead to cell and tissue damage, contributing to aging and chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and eye diseases.
The Science Behind Oxidative Stress
Free radicals can cause oxidative stress by damaging DNA, proteins, and cell membranes. This damage can lead to a range of chronic conditions. Antioxidants, which are either produced by the body or ingested through diet, neutralize free radicals by donating an electron, thus preventing them from causing harm. The balance between oxidative stress and antioxidants is crucial for maintaining overall health and longevity.
A landmark study published in the "Journal of Clinical Investigation" highlighted the role of oxidative stress in chronic inflammation and linked diseases (Pham-Huy, He, Pham-Huy, 2008). This study showcased how oxidative stress can activate a variety of transcription factors, leading to the expression of over 200 genes, including those for inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules.
Causes of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress can be caused by several factors, including:
- Environmental pollutants: Exposure to pollutants, radiation, and tobacco smoke can increase the production of free radicals.
- Diet: Consuming excessive amounts of certain foods, especially those high in fats and sugars, can promote oxidative stress.
- Lifestyle: Excessive alcohol consumption, lack of physical activity, and chronic stress can contribute to oxidative stress.
- Chronic conditions: Diseases like diabetes and obesity can exacerbate oxidative stress.
Health Effects of Oxidative Stress
The repercussions of oxidative stress on health are profound. It's implicated in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, as shown in a study in "Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology" (Stocks, Gutteridge, 2013), indicating how oxidative modification of LDL cholesterol plays a pivotal role in the development of this condition. Furthermore, oxidative stress has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases through its ability to damage neurons, as discussed in "Free Radical Biology and Medicine" (Halliwell, 2006).
Prevention and Management

Managing oxidative stress involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and dietary interventions:
- Antioxidant-rich diet: Consuming foods high in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, can help balance free radicals.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can enhance the body's antioxidant defense system.
- Reducing exposure to toxins: Minimizing exposure to environmental pollutants and smoking can decrease free radical production.
- Stress management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce oxidative stress by lowering the physiological stress response.
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development of various chronic diseases. Understanding its causes and effects can help in devising strategies for prevention and management. By incorporating a healthy lifestyle and diet, individuals can mitigate the impact of oxidative stress, promoting overall health and longevity. We recommend sticking to a Mediterranean diet with an emphasis on plant based ingredients to assist in the reduction of free radicals.
As always please consult your healthcare practitioner before starting a new dietary program or lifestyle change.

1 comment
It is very interesting to learn about oxidative stress thanks